- Knowledge Overview
-
Among the production processes of bamboo products, making bamboo strips is one of the most time-consuming tasks for producers. Mechanizing this process will greatly improve production efficiency in product processing. The bamboo processing machinery used in the process of making bamboo strips was developed in Japan in the 1940s. At that time, many domestic producers of bamboo products used the technology, and it was also introduced to public vocational training institutions and knowledge was spread to other Asian countries.
Japan’s unique and outstanding technological capabilities were utilized in the development and practical application of bamboo processing machinery for processing bamboo, a natural material. Bamboo processing machines such as round bamboo splitters, bamboo splitting machines, and bamboo peeling machines can be classified according to the process of making bamboo strips. This Knowledge Project will target on the bamboo peeling machines, which have been most widely used to date in the bamboo strips manufacturing process.
- Background (history and development)
-
Bamboo grows throughout Japan and they are classified into 131 groups, including madake (Phyllostachys), moso bamboo, and hachiku, which grow wild or in cultivation. Several useful species have been used as tools for daily life in agriculture and fishing, and rantaishikki (urushi lacquer ware made by bamboo) has been excavated from Jomon-era ruins. Its history can be traced back at least several thousand years.
In Japan’s bamboo product industry, along with the progress of industrialization in society in the 20th century, bamboo processing machines such as round bamboo splitters and bamboo peeling machines were developed and put into practical use. In addition to producers who wanted to save labor, demand from public vocational training institutions supported the development of machine manufacturing technology. One company that is said to be one of the pioneers in this field is Sato Chikuko Manufacturing Co. (current SATO HOLDINGS CORPORATION), which began developing and manufacturing bamboo processing machines in the 1940s based in Saitama Prefecture, and manufactured and sold them to production areas throughout Japan as a specialized manufacturer. On the other hand, different types of bamboo are used for bamboo products depending on the region where they are produced, and different types and shapes of bamboo products are produced. Therefore, development was carried out simultaneously in various regions as a product unique to the region of production.
Currently, demand for bamboo processing machinery has decreased compared to a certain period. However, in the bamboo products industry, where a shortage of workers is an issue, bamboo processing machines help save labor and continue to be used in various regions. In the area around Beppu City, Oita Prefecture, the largest producer of madake (Phyllostachys), producers and local ironworks collaborated after the war to develop and manufacture bamboo peeling machines, and the machines from that time can still be seen being used today. One manufacturer in Oita City inherited the know-how and is still manufacturing to order.
- How to Apply Knowledge
-
Bamboo peeling is a process in which round bamboo is first split into strips and then separated into the skin and body to the thickness of the strips used for weaving.
The structure of a typical bamboo peeling machine is that the bamboo material is inserted between a pair of upper and lower rotating rollers with rubber on the surface to create a strip, and then it carries the bamboo material from the front side to the back as seen by the operator (Figure 1). Between a pair of rollers installed at several locations and the next pair of rollers, a blade adjusted in advance to an appropriate angle is installed, and when the bamboo material hits the blade, it is peeled to the skin side/the body side or the width is aligned (Figure 2). The structure is relatively simple, and the only consumables are the rubber on the rollers and the belt connected to the motor, which make maintenance easy. However, adjusting the position and angle of the blade according to the size of the strip to be made and the bamboo material requires a certain level of skill and experience, and is quite time-consuming. Therefore, sometimes multiple machines adjusted to a standard size may be prepared to save the time and effort of making adjustments each time.

Figure 1. Bamboo peeling machine Takehigo (thin strip of bamboo) passes between the upper and lower pairs of rollers.
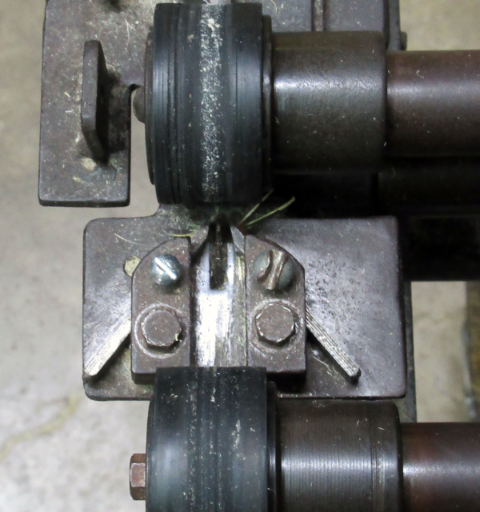
Figure 2. Blade to adjust the width between rollers. Adjust the width with screws.
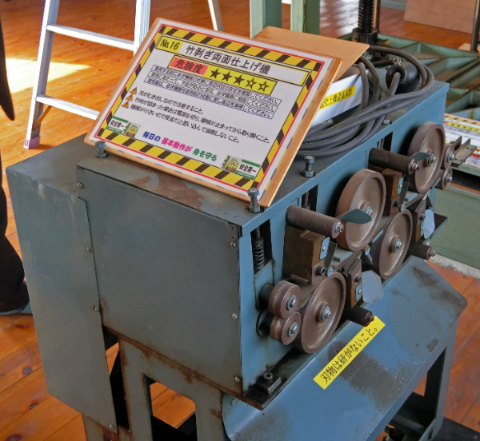

Figure 3. Bamboo peeling and double-sided finishing machine. Upper and lower blades finish bamboo to a certain thickness The general process of making bamboo strip is described below, along with the manual process. It is possible to replace steps (3) to (7) with a bamboo peeling machine. However, the number and order of processes may be changed depending on the products. There may also be differences between manual and machine processing.
There are two types of bamboo peeling machines: one for rough peeling, which is used at the beginning, and one for thin peeling, which is used for finishing. Some products for peeling are equipped with multiple blades so that width cutting and chamfering can be done at the same time.
- Preparation of materials: removing dusts from surfaces and knots, etc.
- Rough split: Split the round bamboo in the direction of the fibers.
- Rough peeling: peeling the skin and the body.
- Small split: Split in the direction of the fiber to make it even finer.
- Thinly peeled: Remove the skin and body further and make it thin to about 0.5 mm.
- Width trimming: Align the width of the bamboo strips to the required width.
- Chamfering: Cutting off the corners of bamboo strips.

Figure 4. Bamboo processing machinery in operation. At NAGAI SEICHIKU Inc., (Beppu city) - Examples of Applying Knowledge
-
Among the production processes for bamboo products, which include cutting down bamboo, removing oil, making bamboo strips, and weaving them, making bamboo strips is one of the most time-consuming tasks for the producers. Mechanization will greatly improve production efficiency in product processing. Bamboo processing machines were developed for each process of making bamboo strips, including round bamboo splitters, bamboo splitters, and bamboo peeling machines, but the most widely used to date is the bamboo peeling machine.
The main customers for bamboo processing machinery were producers of bamboo products, as well as public vocational training institutions, welfare facilities, and industrial testing centers throughout the country. The bamboo peeling machines are still active at the training institute and are available on an hourly rental basis to producers who wish to use them.
The technology for using bamboo peeling machines was introduced to Taiwan, where Japan established a bamboo processing school to develop and teach the technique, and to Southeast Asian countries as part of the post-war reparations business. It was brought to Southeast Asia along with rattan processing machinery and palm processing machinery. Later, there were reports that machines manufactured in Taiwan, where technology was passed down from Japan, were being used in India, and it appears that the technology has spread to a variety of countries and regions. In Vietnam, which is currently Japan’s main import partner for bamboo products, bamboo peeling machines with the same mechanism as Japanese machines are being use.
There are many types of bamboo, and each type has different characteristics such as thickness, hardness, and its knot height. Therefore, when introducing bamboo processing machinery to different countries and regions, adjustments and modifications are necessary to accommodate the type of bamboo used locally.
- Positioning and Characteristics of Knowledge in Japan
-
Mechanization was explored in Japan’s bamboo product industry as industrialization progressed in the 20th century. In particular, as a solution to the wartime shortage of workers, efforts were made to develop machines such as round bamboo splitters, bamboo splitters, and bamboo peeling machines, with the aim of reducing the labor involved in the labor-intensive process of making bamboo strips. Bamboo is a natural material, so its size and shape vary depending on the individual, and it is hollow inside and the processed parts are thin. Therefore, the development and commercialization of bamboo processing machinery is a field in which Japan’s unique and outstanding technological capabilities are utilized.
Due to the decline in demand for bamboo products in Japan, the demand for bamboo processing machinery has gradually decreased, and even now there are only a limited number of manufacturers who have the manufacturing technology. On the other hand, in addition to producers of bamboo products, Japanese environmental citizen groups have also purchased bamboo peeling machines to make effective use of bamboo harvested through bamboo forest maintenance activities, and have used them to make bamboo products, and have demonstrated their use to the general public.
- Owners/inheritors of knowledge
-
In Japan, students are taught how to use bamboo processing machinery at specialized bamboo craft schools. For example, Oita Prefectural Bamboo Crafts Training Center offers a course in bamboo crafts (capacity of 12 students, training period of 2 years). Beppu City Traditional Bamboo Crafts Center provides bamboo classes and machinery for city residents. Traditional Arts Super College Of Kyoto (Nantan City, Kyoto Prefecture) offers a course in bamboo crafts.
The “Automatic Takehigo (thin strip of bamboo) Manufacturing Machine” was filed as a patent in 2005. Application No. 2005-061753, Publication No. 2006-240195.
- Related URLs (in Japanese)
-
- Beppu Bamboo crafts Cooperative Association Website: https://www.beppu-take-kumiai.com/index.htm (Reference: 1/5/2021)
- Beppu City Traditional Bamboo Crafts Center Website: https://takezaikudensankaikan.jp/ (Reference: 1/5/2021)
- Oita Prefectural Bamboo Crafts Training Center Website: https://www.pref.oita.jp/site/280/ (Reference: 1/5/2021)
- Blog of “TAKETORA Yamagishi Bamboo Co.”
https://www.taketora.co.jp/diary/2012/12/post-2158.html (Reference: 1/5/2021)
- Other
-
Bamboo products, which are expected to be a candidate for forest business products in Asian countries, grow quickly and require fewer years to be converted into cash than timber and other materials. For this reason, it is a product that is compatible with community-participatory forest management systems that are being promoted in various countries as forest conservation policies. On the other hand, in developing countries in general, low productivity in the production of bamboo products is one reason why producers are unable to increase their profits. If bamboo products grow into a more profitable forest business through the introduction of bamboo processing machinery, it can be expected to strengthen forest conservation incentives.
Website URL:https://www.acl.or.jp/contact/
Your Knowledge could start making a change, when issue is faced; in forest conservation, or in value chains to use forest resources in a sustainable way.


Your Feedback.